Analogue vs Digital Two-Way Radios - What's The Difference?
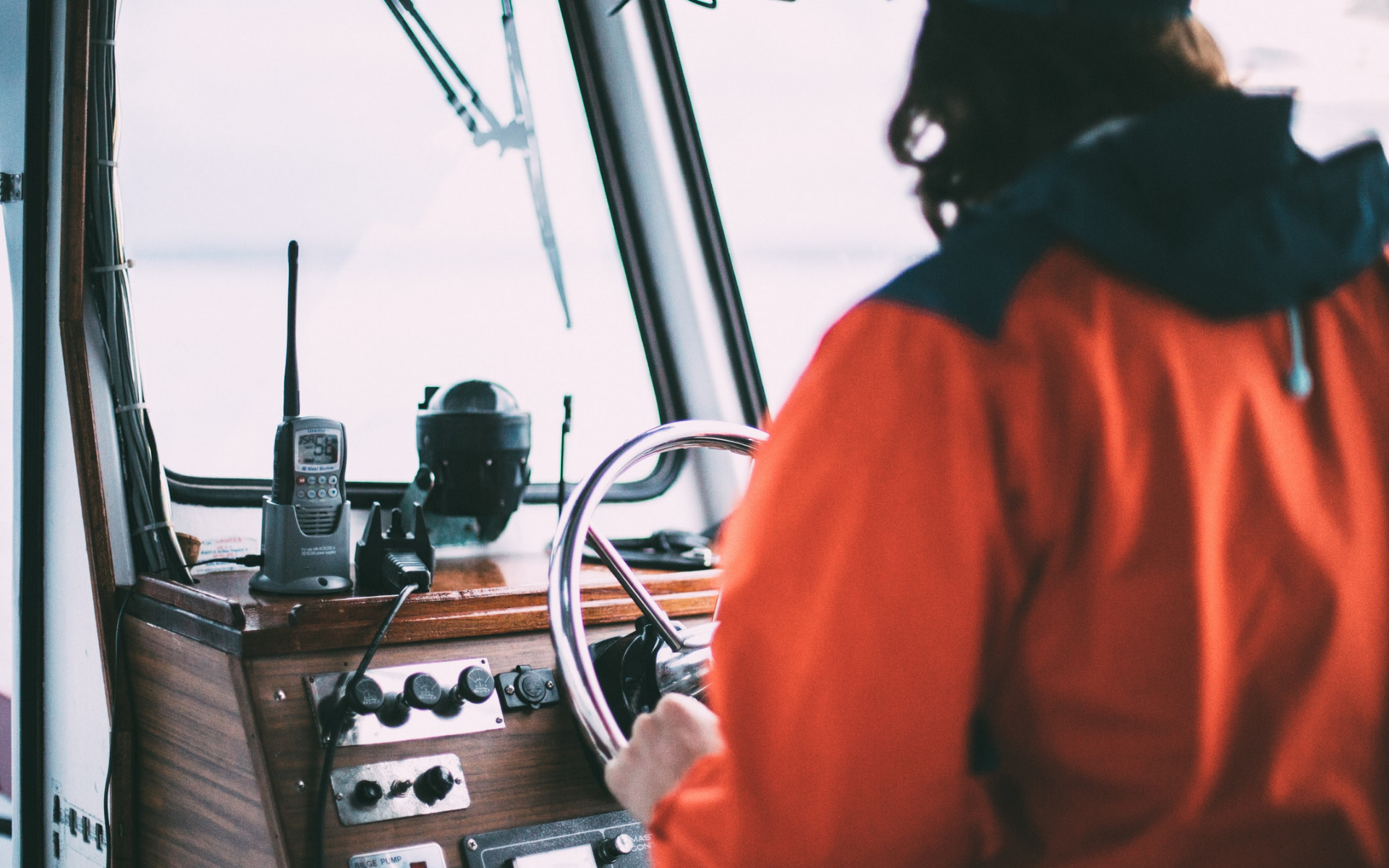

Two-way radios are key players in keeping people safe and allowing for easy communication across a wide land area and several team members. They are often used by farmers, trades, and event staff but more recently have been adopted by museums, retail stores, and hospitality, while individuals also utilise them on private boats. While they are useful for events and day-to-day delivery of services, they are also life-saving tools that allow people to report incidents and reach emergency care.
The main decision when it comes to choosing a two-way radio for a business is, do we need analogue or digital radios? What’s the difference and what is better for me? Well, let’s take a look.
![Bus Dispatcher CB Radio [Tait Communications]](https://images.ctfassets.net/mplktqcfflsk/3eMy1lo4i70Qm4heVWuivH/e5394517e18bd9b1cbd80795d9e8e885/Bus_Dispatcher.jpg?w=800&h=533&fl=progressive&q=85&fm=jpg&bg=transparent)
Analogue Radio
Analogue radios are operated in what some people might describe as the ‘traditional’ way, they’ve been used as trusted communications since the 1930s. They use frequency modulation (a fancy way to say changing the radio wave frequency to carry the audio) to transmit the sound to another radio.
These are often quick and easy solutions to implement in a workplace and they are more cost-effective. But with savings comes expenses in terms of features. Analogue microphones transmit every sound they pick up, including unwanted background noise. They also have a smaller area of coverage and only allow one two-way conversation per channel at that time, meaning they just won’t work as well for some teams.
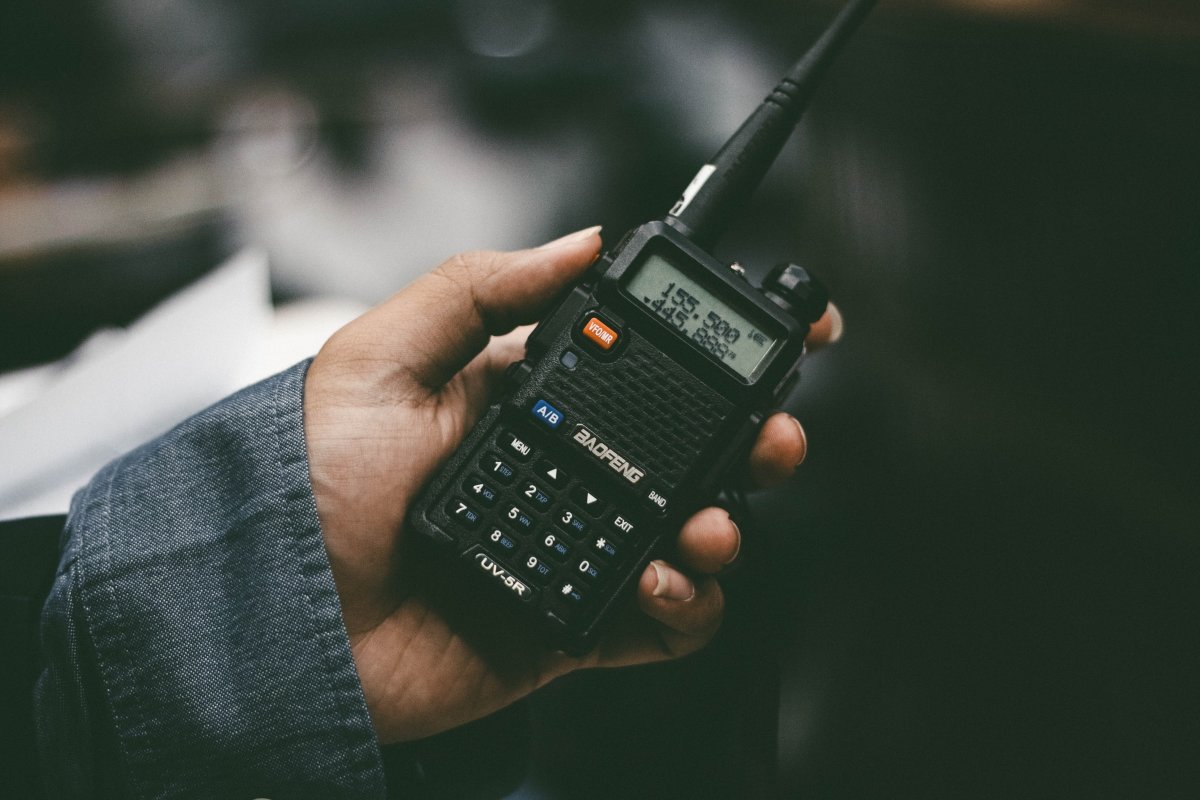

Digital Radio
While analogue radios use older radio wave frequency tech, digital radios use a mathematical system that uses binary. Binary describes a numbering scheme in which there are only two possible values for each digit: 0 and 1. Binary in digital encoding/decoding systems is when there are exactly two possible states.
Sound pretty flash right? The digital radios can turn this binary code from the voice into a digital transmission to other radios. This makes the voice transmission very clear right up until the edge of the coverage area. They can even switch between digital and analogue if you need to communicate with someone on an analogue radio!
Digital radios also have a few other awesome upgraded features from the analogue style:
Bigger bandwidth capacity! This means you can have more people talking on your channel than if you were using analogue radios.
Better coverage. You can go further and better with digital, meaning a safer and cleaner communications line.
Longer battery life. Who doesn’t love having a better battery to last you longer? No one likes having their devices die on them!

Where to now?
While businesses are still enjoying and functioning well with analogue, a lot of businesses are phasing them out to prepare for a fully digital radio using workplace. Digital has several additional integrated apps to help create a smooth operational approach for things like security, ticketing, events, and dispatching. However, analogue is a quick, cost-effective way to bring two-way radios in a business.
MOTAT is also embarking on this journey. Several teams in the museum use two-way radios to communicate across our sites. We hope to have our analogue radios switched to digital in 2022!
And for all the radio fans out there, tune in to MOTAT's radio collection highlight!
LINK: 100 years of New Zealand radio broadcasting
Story by Makayla Wallace-Tidd, Communications Coordinator, MOTAT
Citation:
Wallace-Tidd, Makayla. Analogue vs Digital Two-Way Radios - What's The Difference? MOTAT Museum of Transport and Technology. First published: 16 February 2022. URL: https://www.motat.nz/collections-and-stories/storiesanalogue-vs-digital-two-way-radios-whats-the-difference